As plastic pollution continues to threaten our planet, there has been a growing interest in bioplastics as a more sustainable alternative. In this article, we will explore what bioplastics are, their benefits, and their different types.
What are Bioplastics?
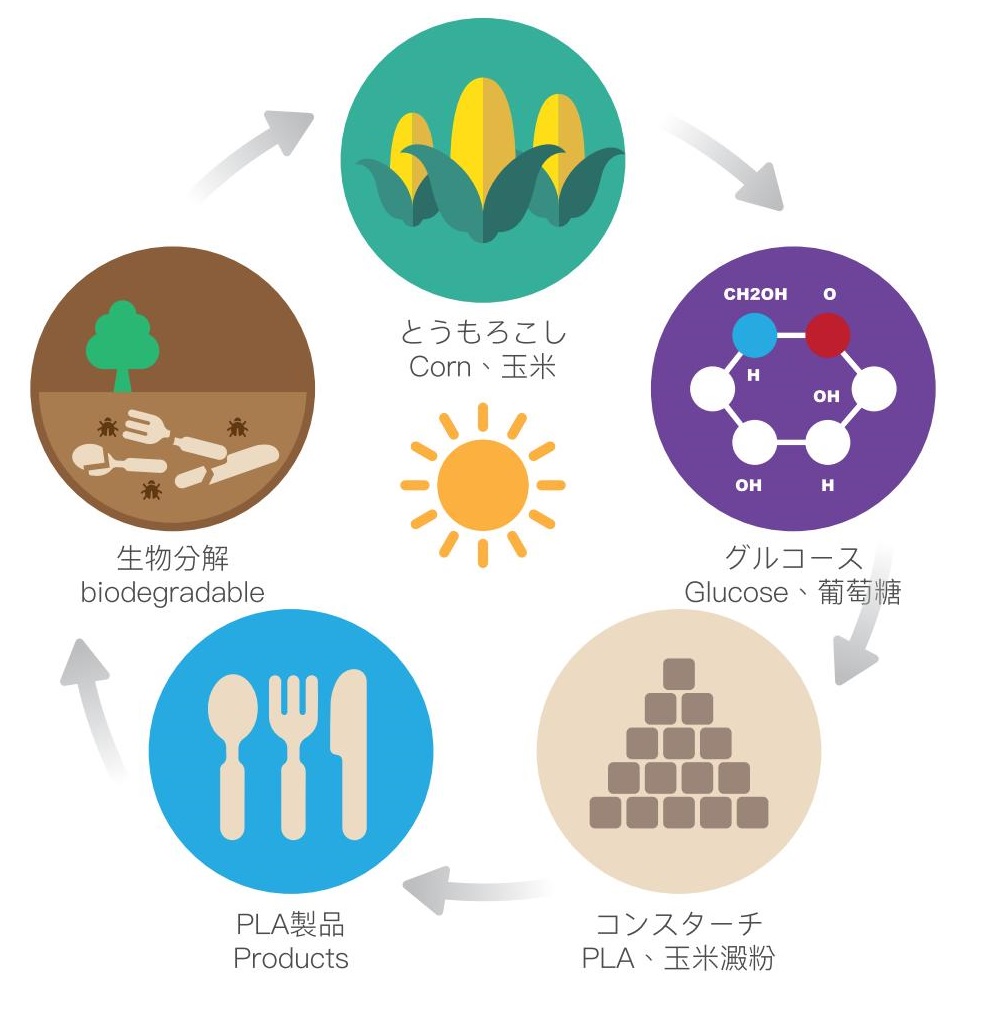
Bioplastics are plastics that are made from renewable resources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, and pea starch. Unlike traditional plastics that are made from fossil fuels, bioplastics are biodegradable and compostable. They can be broken down by microorganisms and return to the soil, reducing plastic pollution in the environment.
?Know more about Recycled Plastic Products :Recycled Plastic Products in Our Daily Life
Benefits of Bioplastics
One of the main benefits of bioplastics is their reduced environmental impact. Unlike traditional plastics, bioplastics are made from renewable resources and are biodegradable. This means that they do not contribute to the buildup of plastic waste in the environment. Bioplastics also have a smaller carbon footprint than traditional plastics, as they produce less greenhouse gas emissions during production.
Types of Bioplastics
There are two main types of bioplastics: biodegradable and non-biodegradable. Biodegradable bioplastics can be broken down by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. They can be further divided into two categories: compostable and oxo-biodegradable. Compostable bioplastics can fully biodegrade in a composting environment, while oxo-biodegradable bioplastics require a certain level of oxygen exposure to degrade. Non-biodegradable bioplastics, on the other hand, are made from renewable resources but do not biodegrade. They can be recycled or incinerated to generate energy.
Applications of Bioplastics
Bioplastics can be used in a wide range of applications, such as packaging, agricultural films, disposable utensils, and even automotive parts. As bioplastics continue to evolve, they are becoming more versatile and can be used in more demanding applications. For example, some bioplastics can now be used in the production of durable goods, such as cell phone cases and furniture.
At Green Value, we are committed to sustainability and have developed a range of bioplastic products. Currently we have container products which are made from high-quality biodegradable bioplastics that are compostable and safe for the environment. We also have tableware made from corn starch. Green Value offer a wide range of products, from packaging materials to consumer goods, and we are continually exploring new applications for bioplastics.
Bioplastics offer a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, and their use is becoming increasingly popular as individuals and companies seek to reduce their environmental impact. As the demand for bioplastics continues to grow, we can expect to see more innovative products and applications in the future. At Green Value, we are proud to be part of this movement and offer a range of high-quality bioplastic products to meet the needs of our customers.
?Know more about various Green Plastic Solutions :Recycled Plastic Manufacturing
Q&A
Q1. Does biodegradable material have to be decomposed in a composting environment?
Ans: Biodegradable materials undergo two main stages of decomposition. In the first step, hydrolysis occurs, breaking down the high molecular weight biodegradable polymer into oligomers with molecular weights in the thousands. These oligomers are then digested by soil microorganisms and their enzymes to produce carbon dioxide and water. The hydrolysis reaction requires a high humidity environment and a temperature of around 50-60 degrees Celsius to proceed quickly and achieve 90% decomposition within 180 days. If the biodegradable material is in a general river or marine environment, the decomposition time will be slower (since the ambient temperature is generally 15-30 degrees Celsius), and will take several years to decompose instead of the perceived inability to decompose.
Q2. Will the widespread use of bioplastic materials lead to food shortages?
Ans: In the past, bioplastic materials were mainly made from corn, which did cause a problem of diverting crops away from food production. However, in the last 10 years, the focus has shifted towards using plants that can be grown on marginal land, such as cassava, castor, and algae grown in the ocean. In addition, there has been progress in scaling up the production of bioplastics from agricultural waste using biological fermentation.
Ask for a quote: sustainable plastic manufacturing, bioplastic, biodegradable plastic, green plastic, PLA plastics.



